pleural effusion cat ultrasound
Four standard effusion types recognized in addition to blood. The pleural effusion volume was calculated volumetrically from the CT scan data.

Pdf Thoracic Ultrasound A Method For The Work Up In Dogs And Cats With Acute Dyspnea Semantic Scholar
The aims of ultrasound guided assessment of pleural effusion are.

. Additional findings in patients with pyothorax may include depression anorexia weight loss dehydration muffled heart and lung sounds and pale mucous membranes. Although the application of ultrasound on the thorax can be limited by aerated lung in normal individuals acoustic window is created with the presence of pleural effusion and non-aerated lung in diseased patients 14For dogs and. Other signs are loss of sharp silhouette of the ipsilateral hemidiaphragm and thickening of the minor fissure.
The therapeutic intervention also provides your first diagnostic test. For those who are new to imaging around the heart with ultrasound differentiating a pericardial from a pleural effusion can be tricky particularly when the pleural effusion is circumferential around the heart. The type of pleural fluid withdrawn will enable your veterinarian to diagnose the cause of the pleural effusion.
The chest wall may seem incompressible in cats with thoracic effusion. Ultrasound protocols are highly sensitive and specific for the detection of pleural effusion alveolar interstitialsyndromeandpneumothorax. Ultrasound-guided pleural effusion drainage by catheter insertion is a safe and effective procedure.
Ultrasound can be used in the assessment of pleural effusion volume. Normally a small amount of fluid is present in the pleural space which serves to lubricate the surfaces and prevent friction as the lung expands and deflates. Each of these 3 ultrasound formats has.
In some cases ultrasound may also be. Four criteria have been described to differentiate ascites from pleural effusion by CT. Abdominal ultrasounds were performed in 70 cats with pleural effusion and revealed concurrent abdominal effusion in 59 of these cats.
Pleural fluid is often represented as a hazy opacity of one hemithorax with preserved vascular shadows. Found with right congestive heart failure obstruction to lymphatic drainage by tissue adhesions in pleural space lung lobe torsion neoplasms and abdominal contents herniating. The trocar technique is faster and easier.
Both the trocar and the modified Seldinger techniques can be used. Abdominal abnormalities identified on ultrasound included abdominal masses lymphadenopathy hepatic venous congestion hepatomegaly splenomegaly renal enlargement small intestinal wall thickening steatitis and pancreatitis. Measurement of a pleural effusion volume with point-of-care ultrasonography may be a useful tool for intensivists and is an active area of research in critical care 7.
Overview of Pleural Effusion in Cats Pleural effusion is an abnormal accumulation of fluid in the pleural space which is the cavity between the lungs and the thoracic wall. Ultrasound has become a common diagnostic procedure in small animal clinical medicine over the past decades. The caudal vena cava cvc is seen extending from the liver L to the heart H.
If the FAST ultrasound does reveal pleural effusion thoracentesis can be carried out. Ultrasonography is superior to chest radiography in detecting the presence of pleural effusions and in distinguishing pleural effusions from atelectasis or pleural thickening. There are a number of characteristic findings on radiographs that will help your veterinarian identify the presence of pleural effusion.
Compared to chest computed tomography CT scan pleural ultrasound has 93 sensitivity and specificity for detecting pleural effusions. Fluid Scoring System TFASTÒ for the detection of pleural and pericardial effusion pneumothorax and its 4 TFASTÒ echo views and Vet BLUEÒ the veterinary brief lung ultrasound exam a regional pattern-based approach with its B-line Scoring System and its Visual Lung Language. A sample of pleural fluid obtained by piercing the cats chest cavity with a needle will be sent to the laboratory for analysis.
To characterize the effusion noting echogenicity of the fluid any loculations solid masses and pleural disease. Cats with pleural effusion often have severe respiratory compromise at presentation. In the latter situations therapeutic intervention must be initiated quickly to prevent respiratory arrest.
The ultrasound US examination was performed less than 6 h after the diagnostic CT scan. The transducer is perpendicular to the ribs. Accumulation of fluid in the pleural space.
Pleural effusion is typically diagnosed by taking radiographs X-rays of the chest. This procedure removes excess fluid from the pleural space using a needle which not only relieves pressure on your cats lungs but also provides your veterinarian with pleural fluid samples. In the following article we present two cases concluding with a third case in which both types of effusion can be seen simultaneously.
The appearance of the hematocrit sign may be observed in hemothorax with a surface layer of anechoic fluid sitting atop a settled fine echogenic sediment. Pleural effusions can be entirely overlooked on supine radiographs or can be misdiagnosed as pulmonary consolidation or atelectasis. Thoracic radiographs usually reveal pleural effusion.
Cats presenting with pleural effusion are nearly always in respiratory distress ranging from an increased respiratory rate and effort to open mouth breathing. The success rate is low when the effusion is loculated and septated. To mark the optimal site for drainage and perform the procedure if required.
Refer to the article Pleural effusion volume ultrasound for more information. X-ray and ultrasound imaging of the chest cavity are also very helpful in analyzing the causative factors. Unlike with a pericardial effusion in the case of accumulation of fluid in the pleural space there is no collapse of the heart walls.
In the below clip from the Sonoscape S2 you can actually see the separation of the right ventricular free wall from the pericardium in a cat. These four signs the diaphragm sign the displaced crus sign the interface sign and the bare area sign are reliable when only one abnormal fluid collection is present. Screening for effusions can be.
To determine and describe the size and site of the effusion. Both computed tomography CT and ultrasound US can be used to differentiate ascites from pleural effusion. B Longitudinal ultrasound scan of the caudal thorax of a cat with pleural effusion.
In controlled settings ultrasound may detect constitutive pleural fluid can reliably detect effusions 20 mL in clinical settings and may approach the sensitivity and specificity of computed tomography. Caudal is to the left of the image. Within 458 - 287 h after the CT scan all patients were re-examined with US in the ICU.
In contrast to humans veterinary studies have shown questionable sensitivity and specificity for TFASTandVet BLUEtodetectpleuralspaceandlungpathology12. Pleural effusion is present in both hemithoraces e. Careful handling and prompt and adequate stabilisation incorporating supplemental oxygen.
The transducer is perpendicular to the ribs.

Sonography Assessment Overview Of Afast And Tfast Today S Veterinary Practice

Differentiating Pericardial From Pleural Effusion Animal Ultrasound Association
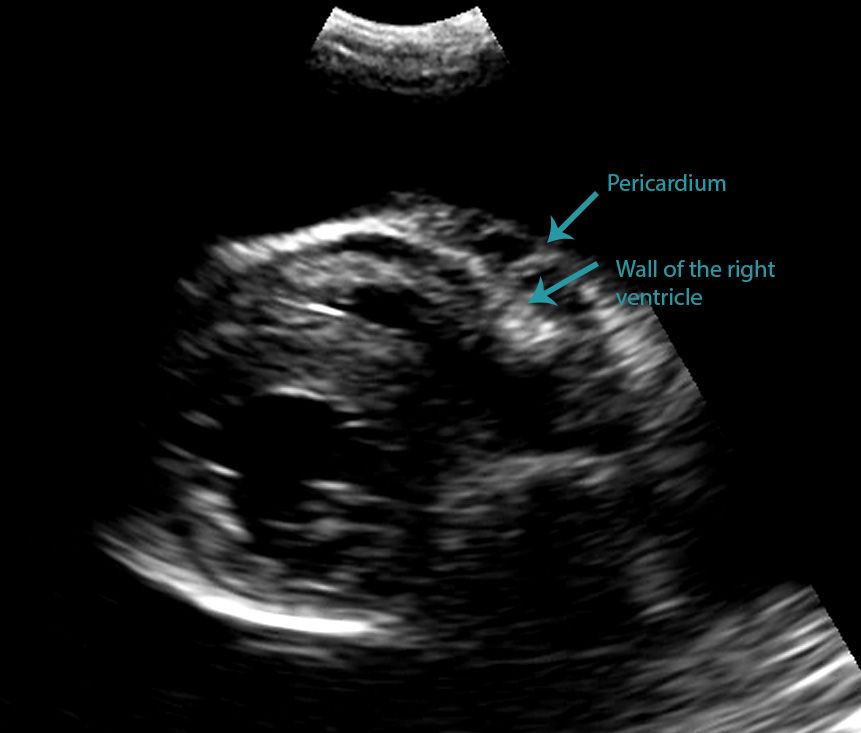
Differentiating Pericardial From Pleural Effusion Animal Ultrasound Association

How To Ultrasound Detection Of Pleural Fluid Case Study Video Youtube

Veterinary Echocardiography Newsletter 1 Effusions Animal Ultrasound Association

Different Types Of Pleural Effusion On Ultrasound Scan A Exudate B Download Scientific Diagram

Differentiating Pericardial From Pleural Effusion Animal Ultrasound Association